Do AI Chatbots like ChatGPT Pose a Cybersecurity Risk?
If you're a human alive in 2023, chances are you've heard the news: ChatGPT is changing the world. Capturing the interest of everyone from marketers to the programming community, the release of ChatGPT (and now GPT-4) undoubtedly marks a seminal moment in the world of technology and artificial intelligence.
Remarkably becoming the fastest growing consumer application in history, much has been made of the myriad benefits that chatbots such as this will bring. Although, these benefits are certainly undeniable (and many quite miraculous), the following is a discussion about some of the possible information and cyber security risks associated with ChatGPT.
Want to protect your organisation from cybercrime?
We can help you get started - let's have a chat.
What is ChatGPT?
ChatGPT is a Large Language Model (LLM) developed by American research organisation OpenAI. Released to the public late last year, the system is based on the GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) architecture, a type of deep learning model designed for natural language processing tasks such as language translation, text summarisation, and text generation.
Trained on a massive amount of text data, including books, articles, and websites, LLMs like ChatGPT are AI systems which typically utilise unsupervised learning methods; a training process based on patterns and relationships between words and phrases.
By providing ChatGPT with a prompt, usually a question, the underlying algorithm generates a response based on probabilistic calculations derived from training data.
For example, when asked to finish the following sentence fragment, "March 14th is perhaps most well known as the date of...", in this particular instance, ChatGPT responded "...Pi Day, which is a celebration of the mathematical constant π (pi) and is observed on March 14th (3/14) each year."
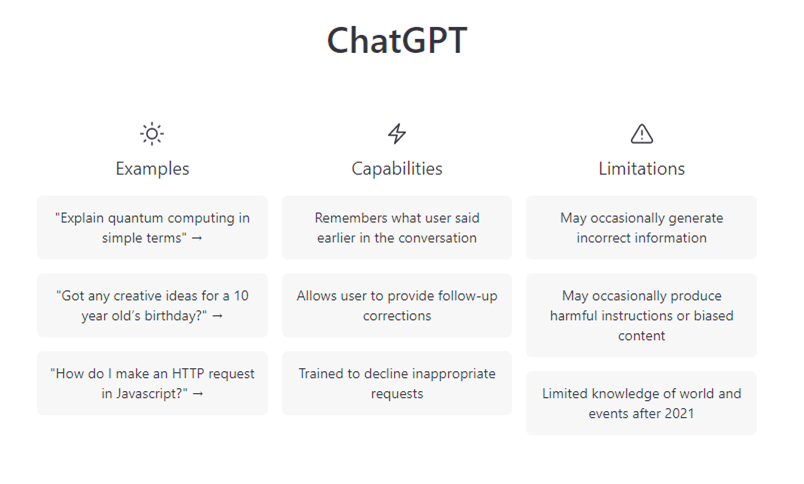
Although very impressive, the system is not without its limitations, and as OpenAI themselves acknowledge, the algorithm is more than capable of responding to users with incorrect information (sometimes known as 'hallucinations').
As well as occasionally mixing up facts, ChatGPT can in some instances be prompted to output offensive or 'harmful' content, and has similar to other platforms, been accused by some of political bias; and while these are certainly reasonable concerns, the platform may also pose less obvious risks.
Cyber Security and ChatGPT
Cyber Criminals
As well as helping users with innocuous or benign problems, chatbots can also be used for malicious purposes. For instance, LLMs can replicate writing styles on demand, which presents a risk of criminals using LLMs to write convincing phishing emails, including emails in multiple languages.
There have also been some experiments which have shown that by "insisting and demanding", users can bypass platform filters and essentially bully ChatGPT into producing some rather sophisticated malware.
Similarly, LLMs may also provide technical assistance to cyber criminals. Just as LLMs are being used by many legitimate users to provide detailed answers to specific technical queries, the risk is that criminals can use these capabilities to sinister ends.
For instance, if an attacker is struggling to escalate privileges or find specific data, they could ask an LLM, which may provide partially correct answers that a traditional search engine would not, thus helping the criminal party worsen the severity of their attack.
Data Privacy
As an AI language model, ChatGPT itself does not have direct access to user data, and its interactions are currently limited to text-based conversations. However, ChatGPT's use and deployment could have implications for data privacy in several ways.
Firstly, ChatGPT was trained on a vast corpus of text data, some of which may contain personal information. While efforts were made to anonymise and obscure such data, given the scale of the training, it's fair to assume not all was caught.
Although there are currently no reported cases of 'data leakage', given the experimental nature of this new technology, it is not beyond the realm of possibility that we could see sensitive training data inadvertently making its way into outputs.
Furthermore, and perhaps the most immediate worry, is when users interact with ChatGPT, they could potentially provide personal information, such as their name, location, or email address.
While ChatGPT does not (as of writing) automatically incorporate queries into its model, user inputs are stored and visible to OpenAI, and are likely to be used in platform development at some point in the future, meaning, personal data could increasingly be introduced to the system, despite efforts to avoid this situation.
Should I be Afraid?
As these new technologies are unleashed upon the world, they will undoubtedly bring all kinds of new security concerns with them. Regardless of efforts to minimise these risks, as we've seen with other cutting-edge technologies, side effects remain unavoidable.
While these speculative risks should not go unacknowledged, users should currently be most wary of inputting sensitive, or personal data.
For instance, in a recent developer live stream, OpenAI demonstrated the amazing capabilities of GPT-4 in providing detailed feedback regarding a tax related query. Though, in this instance no real personal financial information was given to the system, some number of users will inevitably be reliant on LLMs to ease the burden of similarly complex calculations.
With various organisations pushing to release their own LLMs (including Google's Bard and Meta's LLaMa), how sensitive data will be stored, processed, and potentially monetised, remains to be seen.
In the meantime, users who choose to experiment with these burgeoning technologies would be advised to proceed carefully regarding the kinds of data they submit, and with whom they entrust it.
Security Awareness for your Organisation
Enjoyed our blog? Learn more about how Hut Six can help improve you security awareness with training and simulated phishing. Start a free trial now, or book a meeting with one of our experts.
Featured
How Do I Get Cyber Essentials Certified?
Learn how to obtain Cyber Essentials certification and enhance your organization's cybersecurity posture with our comprehensive guide. Our expert insights will help you navigate the certification process to meet the requirements for Cyber Essentials.
Essential Steps for Security Awareness Training
Starting a security awareness training campaign? Here are 5 essential steps to help ensure information security success.
Malicious Insider Threats - Meaning & Examples
Malicious insider threats can cause massive problems. Here we examine some of the motivations behind attacks and methods of detection organisations can use to reduce risk.
5 Biggest Breaches of 2022 (So Far)
Five of the biggest and most significant data breaches, hacks, and information security attacks of 2022 (so far).
Auditing for GDPR Compliance
Questions to consider when auditing your business or SME for General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) compliance.
Improving Employee Cyber Security
With human error responsible for many breaches and attacks, we offer some helpful areas for improving employee security compliance.
5 Cyber Tips for your Business
Essential cyber tips for helping your business or SME improve information and cyber security.
The Benefits Of Maintaining Compliance For Your Business
By maintaining compliance for your business you can ensure operational efficiency, reduce financial risk, enhance public trust, engage your employees and realise your mission.
Top 5 Phishing Trends in 2022
Insights, trends, and statistics from the world of phishing in 2022.
10 Steps to Cyber Security
The main concepts of the Nation Cyber Security Centre's '10 Steps to Cyber Security' guidance.











